Recent Blog Posts
-
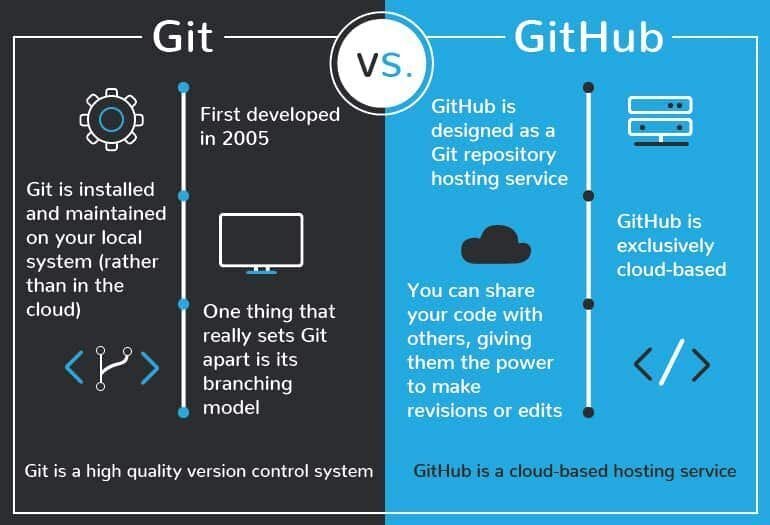
Chapter 14: Pair Programming with Git
•
Techniques for effective pair programming Techniques for effective pair programming involve clear communication, defined roles, and collaboration tools. Pair programming, where two developers work together at one workstation, can significantly improve code quality and knowledge sharing. Here’s how to make it work effectively: Clear Communication Effective communication is the cornerstone…
-

Chapter 13: Using Protected Branches and Required Reviews
•
Implementing branch protection rules Implementing branch protection rules is a critical practice for maintaining the integrity of your codebase, ensuring that only thoroughly reviewed and tested code is merged into important branches like main or master. Branch protection rules can enforce specific workflows, such as requiring pull request reviews before…
-

Chapter 12: Advanced Collaborative Workflows
•
Gitflow workflow The Gitflow workflow is a branching model designed to facilitate parallel development, improve collaboration, and streamline release processes. Developed by Vincent Driessen, this workflow provides a robust framework for managing development and release cycles in projects. It defines a set of conventions for organizing branches and integrating changes,…
-

Chapter 11: Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
•
Introduction to CI/CD pipelines An effective Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipeline is crucial for modern software development, enabling teams to automate processes from code changes to deployment. Here’s an introduction to CI/CD pipelines without using a list: Introduction to CI/CD Pipelines: In software development, CI/CD pipelines are automated workflows that…
-

Chapter 10: Handling Merge Conflicts
•
What are merge conflicts and how they occur Merge conflicts occur when Git is unable to automatically resolve differences between two branches during a merge operation. They typically arise when two or more branches have diverged and Git cannot determine which changes should take precedence. Here’s a detailed explanation without…
-

Chapter 9: Managing Issues and Project Management Tools
•
Using issues to track bugs and feature requests Using issues effectively is crucial for tracking bugs and managing feature requests in a collaborative software development environment. Here’s a detailed exploration of this topic: Introduction: Issues serve as a centralized way for teams to track bugs, discuss improvements, and manage tasks…
-

Chapter 8: Code Review Process
•
Importance of code reviews in collaborative projects In collaborative software development projects, code reviews play a crucial role in ensuring code quality, fostering knowledge sharing, and promoting team collaboration. Here’s an expanded explanation without using a list: Importance of Code Reviews in Collaborative Projects: Code reviews are essential for maintaining…
-

Chapter 7: Pull Requests and Merge Requests
•
Introduction to pull requests In software development using Git, a pull request (often abbreviated as PR) is a fundamental collaboration mechanism for proposing and merging changes into a repository. Here’s an overview without using a list: Introduction to Pull Requests: A pull request serves as a formal request to merge…
-

Chapter 6: Committing Changes
•
Writing good commit messages Crafting clear and informative commit messages is crucial for effective collaboration and project management in Git. Here’s an expanded explanation without using a list: Writing Good Commit Messages: When you make changes to a Git repository and commit them, the commit message serves as a concise…
-

Chapter 5: Forking and Cloning Repositories
•
The concept of forking a repository Forking a repository in Git refers to creating a personal copy of someone else’s repository under your GitHub account. This process allows you to freely experiment with changes without affecting the original repository. Here’s an explanation of forking with an example: Forking a Repository:…





