Recent Blog Posts
-
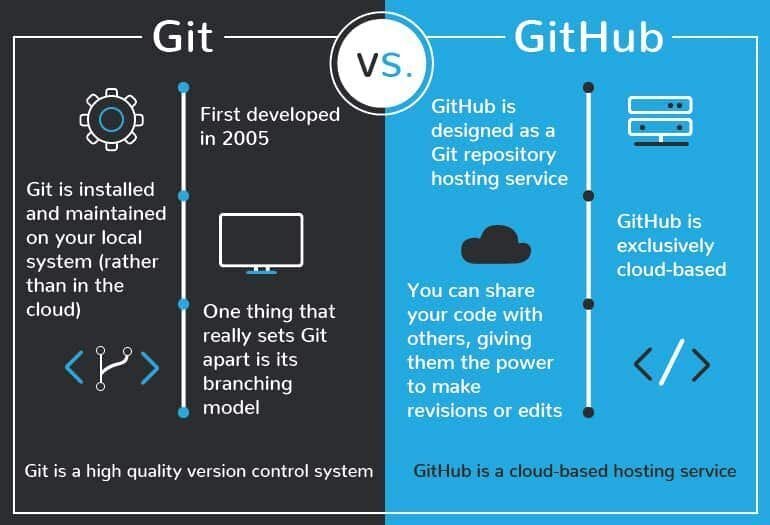
Chapter 4: Branching Strategies for Collaboration
•
What are branches and why they matter Branches in Git are parallel lines of development that allow you to work on different features, fixes, or experiments within the same repository. Here’s an explanation without using a list: In Git, branches serve as distinct lines of development within a repository. Each…
-

Chapter 3: Creating and Managing Repositories
•
Initializing a new repository Initializing a new Git repository is the first step in version controlling your project. It sets up a .git directory where Git stores metadata and objects for tracking changes and histories of your files. To initialize a new repository, navigate to your project directory using the…
-

Chapter 2: Setting Up Your Git Environment
•
Installing Git on different operating systems Installing Git on different operating systems is a straightforward process, but the steps can vary slightly depending on whether you’re using Windows, macOS, or Linux. Here’s how you can install Git on each of these platforms. For Windows, you need to download the Git…
-

Chapter 1: Introduction to Git and Collaboration
•
Understanding the importance of version control in software development Understanding the importance of version control in software development is crucial for maintaining an organized and efficient workflow, especially when multiple developers are involved. Version control systems, like Git, allow teams to track changes to the codebase over time. This means…
-

Appendices:
•
Useful Go Tools and Libraries 1. Build and Dependency Management Tools 2. Testing and Benchmarking Tools 3. Code Quality and Static Analysis 4. IDEs and Editors 5. Web Frameworks 6. Database Libraries 7. Networking and HTTP Libraries 8. Concurrency and Parallelism 9. Utilities and Miscellaneous Conclusion These tools and libraries…
-

Conclusion:
•
Recap of Key Concepts Recap of Key Concepts in Go Programming Basics and Syntax Go is known for its simplicity and efficiency, offering a concise syntax that emphasizes readability and maintainability. Key concepts include: Data Types and Structures Understanding Go’s data types and how they are utilized: Functions and Methods…
-

Chapter 14: Best Practices in Go
•
Code Organization and Project Structure Introduction Code organization and project structure are crucial for maintaining readability, scalability, and maintainability in software projects. This chapter delves into the principles, best practices, and tools for organizing code and defining project structure effectively. Importance of Code Organization Organizing code systematically offers several benefits:…
-

Chapter 13: Deployment and Maintenance
•
Building and Distributing Go Applications Building and distributing Go applications efficiently is a key part of the software development lifecycle. This chapter provides a detailed guide on compiling, building, and distributing Go applications for various platforms. Setting Up Your Go Environment Before you can build and distribute Go applications, ensure…
-

Chapter 12: Advanced Topics
•
Reflection and Generics Reflection in Go Reflection is a powerful feature in Go that allows you to inspect and manipulate objects at runtime. It provides the ability to introspect types, access and modify values, and dynamically invoke methods. The reflect package is the cornerstone of reflection in Go. Basics of…
-

Chapter 11: Testing in Go
•
Writing Unit Tests Unit testing is an essential practice in software development that ensures individual components or functions work as expected. In Go, unit tests are written using the testing package. This section will guide you through the basics of writing unit tests, setting up test files, running tests, and…





